1. Instance Number Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values
| (0020,0013) |
| Required, Empty if Unknown (2) |
| InstanceNumber |
| 1 |
| Integer String (IS) |
|
A number that identifies this image.
Note
This Attribute was named Image Number in earlier versions of this Standard.
2. Image Position (Patient) Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values| (0020,0032) |
| Required (1) |
| ImagePositionPatient |
| 3 |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
The x, y, and z coordinates of the upper left hand corner (center of the first voxel transmitted) of the image, in mm. See Section C.7.6.2.1.1 for further explanation.
Section C.7.6.2.1.1
Image Position (0020,0032) specifies the x, y, and z coordinates of the upper left hand corner of the image; it is the center of the first voxel transmitted. Image Orientation (0020,0037) specifies the direction cosines of the first row and the first column with respect to the patient. These Attributes shall be provide as a pair. Row value for the x, y, and z axes respectively followed by the Column value for the x, y, and z axes respectively.
The direction of the axes is defined fully by the patient's orientation.
If Anatomical Orientation Type (0010,2210) is absent or has a value of BIPED, the x-axis is increasing to the left hand side of the patient. The y-axis is increasing to the posterior side of the patient. The z-axis is increasing toward the head of the patient.
If Anatomical Orientation Type (0010,2210) has a value of QUADRUPED, the
- x-axis is increasing to the left (as opposed to right) side of the patient
- the y-axis is increasing towards
-
- the dorsal (as opposed to ventral) side of the patient for the neck, trunk and tail,
- the dorsal (as opposed to ventral) side of the patient for the head,
- the dorsal (as opposed to plantar or palmar) side of the distal limbs,
- the cranial (as opposed caudal) side of the proximal limbs, and
- the z-axis is increasing towards
-
- the cranial (as opposed to caudal) end of the patient for the neck, trunk and tail,
- the rostral (as opposed to caudal) end of the patient for the head, and
- the proximal (as opposed to distal) end of the limbs
Note
- The axes for quadrupeds are those defined and illustrated in Smallwood et al for proper anatomic directional terms as they apply to various parts of the body.
- It should be anticipated that when quadrupeds are imaged on human equipment, and particularly when they are position in a manner different from the traditional human prone and supine head or feet first longitudinal position, then the equipment may well not indicate the correct orientation, though it will remain an orthogonal Cartesian right-handed system that could be corrected subsequently.
The Patient-Based Coordinate System is a right handed system, i.e., the vector cross product of a unit vector along the positive x-axis and a unit vector along the positive y-axis is equal to a unit vector along the positive z-axis.
Note
If a patient is positioned parallel to the ground, in dorsal recumbency (i.e., for humans, face-up on the table), with the caudo-cranial (i.e., for humans, feet-to-head) direction the same as the front-to-back direction of the imaging equipment, the direction of the axes of this Patient-Based Coordinate System and the Equipment-Based Coordinate System in previous versions of this Standard will coincide.
The Image Plane Attributes, in conjunction with the Pixel Spacing Attribute, describe the position and orientation of the image slices relative to the Patient-Based Coordinate System. In each image frame Image Position (Patient) (0020,0032) specifies the origin of the image with respect to the Patient-Based Coordinate System. RCS and Image Orientation (Patient) (0020,0037) values specify the orientation of the image frame rows and columns. The mapping of pixel location (i,j) to the RCS is calculated as follows:
Equation C.7.6.2.1-1.
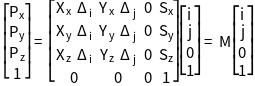
Where:
- Pxyz The coordinates of the voxel (i,j) in the frame's image plane in units of mm.
- Sxyz The three values of Image Position (Patient) (0020,0032). It is the location in mm from the origin of the RCS.
- Xxyz The values from the row (X) direction cosine of Image Orientation (Patient) (0020,0037).
- Yxyz The values from the column (Y) direction cosine of Image Orientation (Patient) (0020,0037).
- i Column index to the image plane. The first column is index zero.
- Δi Column pixel resolution of Pixel Spacing (0028,0030) in units of mm.
- j Row index to the image plane. The first row index is zero.
- Δj Row pixel resolution of Pixel Spacing (0028,0030) in units of mm.
Additional constraints apply:
- The row and column direction cosine vectors shall be orthogonal, i.e., their dot product shall be zero.
- The row and column direction cosine vectors shall be normal, i.e., the dot product of each direction cosine vector with itself shall be unity.
3. Slice Thickness Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values
| (0018,0050) |
| Required, Empty if Unknown (2) |
| SliceThickness |
| 1 |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
Nominal slice thickness, in mm.
4. Slice Location Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values| (0020,1041) |
| Optional (3) |
| SliceLocation |
| 1 |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
Relative position of the image plane expressed in mm.
See Section C.7.6.2.1.2 for further explanation.
Section C.7.6.2.1.2
Slice Location (0020,1041) is defined as the relative position of the image plane expressed in mm. This information is relative to an unspecified implementation specific reference point.
5. Window Center Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values| (0028,1050) |
| Conditionally Required (1C) |
| WindowCenter |
| 1-n |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
Window Center for display.
See Section C.11.2.1.2 for further explanation.
Required if VOI LUT Sequence (0028,3010) is not present. May be present otherwise.
Section C.11.2.1.2
If VOI LUT Function (0028,1056) is absent or has a value of LINEAR, Window Center (0028,1050) and Window Width (0028,1051) specify a linear conversion from stored pixel values (after any Modality LUT or Rescale Slope and Intercept specified in the IOD have been applied) to values to be displayed. Window Center contains the input value that is the center of the window. Window Width contains the width of the window.
Note
The terms "window center" and "window width" are not consistently used in practice, nor were they defined in previous editions of the Standard. The definitions here are presented for the purpose of defining consistent meanings for identity and threshold transformations while preserving the common practice of using integer values for center and width.
Window Width (0028,1051) shall always be greater than or equal to 1.
When Window Width (0028,1051) is greater than 1, these Attributes select the range of input values that are to be mapped to the full range of the displayed output.
When Window Width (0028,1051) is equal to 1, they specify a threshold below which input values will be displayed as the minimum output value.
Note
Whether the minimum output value is rendered as black or white may depend on the value of Photometric Interpretation (0028,0004) or the presence of a Presentation LUT Module.
These Attributes are applied according to the following pseudo-code, where x is the input value, y is an output value with a range from ymin to ymax, c is Window Center (0028,1050) and w is Window Width (0028,1051):
- if (x <= c - 0.5 - (w-1) /2), then y = ymin
- else if (x > c - 0.5 + (w-1) /2), then y = ymax
- else y = ((x - (c - 0.5)) / (w-1) + 0.5) * (ymax- ymin) + ymin
Note
- For the purpose of this definition, a floating point calculation without integer truncation is assumed, though the manner of implementation may vary as long as the result is the same.
- The pseudo-code function computes a continuous value over the output range without any discontinuity at the boundaries. The value of 0 for w is expressly forbidden, and the value of 1 for w does not cause division by zero, since the continuous segment of the function will never be reached for that case.
- For example, for an output range 0 to 255:
-
- c=2048, w=4096 becomes:
-
- if (x <= 0) then y = 0
- else if (x > 4095) then y = 255
- else y = ((x - 2047.5) / 4095 + 0.5) * (255-0) + 0
- c=2048, w=1 becomes:
-
- if (x <= 2047.5) then y = 0
- else if (x > 2047.5) then y = 255
- else /* not reached */
- c=0, w=100 becomes:
-
- if (x <= -50) then y = 0
- else if (x > 49) then y = 255
- else y = ((x + 0.5) / 99 + 0.5) * (255-0) + 0
- c=0, w=1 becomes:
-
- if (x <= -0.5) then y = 0
- else if (x > -0.5) then y = 255
- else /* not reached */
- A Window Center of 2n-1 and a Window Width of 2n selects the range of input values from 0 to 2n-1. This represents a mathematical identity VOI LUT transformation over the possible input values (whether used or not) in the case where no Modality LUT is specified and the stored pixel data are n bit unsigned integers.
- In the case where x1 is the lowest input value actually used in the Pixel Data and x2 is the highest, a Window Center of (x1+x2+1)/2 and a Window Width of (x2-x1+1) selects the range of input values from x1 to x2, which represents the full range of input values present as opposed to possible. This is distinct from the mathematical identity VOI LUT transformation, which instead selects the full range of input values possible as opposed to those actually used. The mathematical identity and full input range transformations are the same when x1 = 0 and x2 is 2n-1 and the input values are n bit unsigned integers. See also Note 7.
- A Window Width of 1 is typically used to represent a "threshold" operation in which those integer input values less than the Window Center are represented as the minimum displayed value and those greater than or equal to the Window Center are represented as the maximum displayed value. A Window Width of 2 will have the same result for integral input values.
- The application of Window Center (0028,1050) and Window Width (0028,1051) may select a signed input range. There is no implication that this signed input range is clipped to zero.
- The selected input range may exceed the actual range of the input values, thus effectively "compressing" the contrast range of the displayed data into a narrower band of the available contrast range, and "flattening" the appearance. There are no limits to the maximum value of the window width, or to the minimum or maximum value of window level, both of which may exceed the actual or possible range of input values.
- Input values "below" the window are displayed as the minimum output value and input values "above" the window are displayed as the maximum output value. This is the common usage of the window operation in medical imaging. There is no provision for an alternative approach in which all values "outside" the window are displayed as the minimum output value.
- The output of the Window Center/Width or VOI LUT transformation is either implicitly scaled to the full range of the display device if there is no succeeding transformation defined, or implicitly scaled to the full input range of the succeeding transformation step (such as the Presentation LUT), if present. See Section C.11.6.1.
- Fractional values of Window Center and Window Width are permitted (since the VR of these Attributes is Decimal String), and though they are not often encountered, applications should be prepared to accept them.
The Window Center (0028,1050), Window Width (0028,1051) and VOI LUT Function (0028,1056) Attributes shall be used only for Images with Photometric Interpretation (0028,0004) values of MONOCHROME1 and MONOCHROME2. They have no meaning for other Images.
If multiple values are present, both Attributes shall have the same number of values and shall be considered as pairs. Multiple values indicate that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If any VOI LUT Table is included by an Image, a Window Width and Window Center or the VOI LUT Table, but not both, may be applied to the Image for display. Inclusion of both indicates that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If multiple Items are present in VOI LUT Sequence (0028,3010), only one may be applied to the Image for display. Multiple Items indicate that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If the VOI LUT Module is defined in an IOD and if neither a VOI LUT Sequence nor a Window Width and Window Center are present, then the VOI LUT stage of the grayscale pipeline is defined to be an identity transformation.
Note
- This requirement is specified so that IODs that define a particular output space for the grayscale pipeline, such as P-Values, are not in an undefined state when no VOI LUT Sequence or Window Width and Window Center are present.
- Despite the Type 3 requirement for VOI LUT Sequence and Window Center, implementations that render images are expected to implement and apply these transformations when they are present in the image, unless overridden by the user, a presentation state, or a hanging protocol, and to allow the user to select which transformation to apply when multiple transformations are present.
6. Window Width Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values| (0028,1051) |
| Conditionally Required (1C) |
| WindowWidth |
| 1-n |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
Window Width for display. See Section C.11.2.1.2 for further explanation.
Required if Window Center (0028,1050) is present.
Section C.11.2.1.2
If VOI LUT Function (0028,1056) is absent or has a value of LINEAR, Window Center (0028,1050) and Window Width (0028,1051) specify a linear conversion from stored pixel values (after any Modality LUT or Rescale Slope and Intercept specified in the IOD have been applied) to values to be displayed. Window Center contains the input value that is the center of the window. Window Width contains the width of the window.
Note
The terms "window center" and "window width" are not consistently used in practice, nor were they defined in previous editions of the Standard. The definitions here are presented for the purpose of defining consistent meanings for identity and threshold transformations while preserving the common practice of using integer values for center and width.
Window Width (0028,1051) shall always be greater than or equal to 1.
When Window Width (0028,1051) is greater than 1, these Attributes select the range of input values that are to be mapped to the full range of the displayed output.
When Window Width (0028,1051) is equal to 1, they specify a threshold below which input values will be displayed as the minimum output value.
Note
Whether the minimum output value is rendered as black or white may depend on the value of Photometric Interpretation (0028,0004) or the presence of a Presentation LUT Module.
These Attributes are applied according to the following pseudo-code, where x is the input value, y is an output value with a range from ymin to ymax, c is Window Center (0028,1050) and w is Window Width (0028,1051):
- if (x <= c - 0.5 - (w-1) /2), then y = ymin
- else if (x > c - 0.5 + (w-1) /2), then y = ymax
- else y = ((x - (c - 0.5)) / (w-1) + 0.5) * (ymax- ymin) + ymin
Note
- For the purpose of this definition, a floating point calculation without integer truncation is assumed, though the manner of implementation may vary as long as the result is the same.
- The pseudo-code function computes a continuous value over the output range without any discontinuity at the boundaries. The value of 0 for w is expressly forbidden, and the value of 1 for w does not cause division by zero, since the continuous segment of the function will never be reached for that case.
- For example, for an output range 0 to 255:
-
- c=2048, w=4096 becomes:
-
- if (x <= 0) then y = 0
- else if (x > 4095) then y = 255
- else y = ((x - 2047.5) / 4095 + 0.5) * (255-0) + 0
- c=2048, w=1 becomes:
-
- if (x <= 2047.5) then y = 0
- else if (x > 2047.5) then y = 255
- else /* not reached */
- c=0, w=100 becomes:
-
- if (x <= -50) then y = 0
- else if (x > 49) then y = 255
- else y = ((x + 0.5) / 99 + 0.5) * (255-0) + 0
- c=0, w=1 becomes:
-
- if (x <= -0.5) then y = 0
- else if (x > -0.5) then y = 255
- else /* not reached */
- A Window Center of 2n-1 and a Window Width of 2n selects the range of input values from 0 to 2n-1. This represents a mathematical identity VOI LUT transformation over the possible input values (whether used or not) in the case where no Modality LUT is specified and the stored pixel data are n bit unsigned integers.
- In the case where x1 is the lowest input value actually used in the Pixel Data and x2 is the highest, a Window Center of (x1+x2+1)/2 and a Window Width of (x2-x1+1) selects the range of input values from x1 to x2, which represents the full range of input values present as opposed to possible. This is distinct from the mathematical identity VOI LUT transformation, which instead selects the full range of input values possible as opposed to those actually used. The mathematical identity and full input range transformations are the same when x1 = 0 and x2 is 2n-1 and the input values are n bit unsigned integers. See also Note 7.
- A Window Width of 1 is typically used to represent a "threshold" operation in which those integer input values less than the Window Center are represented as the minimum displayed value and those greater than or equal to the Window Center are represented as the maximum displayed value. A Window Width of 2 will have the same result for integral input values.
- The application of Window Center (0028,1050) and Window Width (0028,1051) may select a signed input range. There is no implication that this signed input range is clipped to zero.
- The selected input range may exceed the actual range of the input values, thus effectively "compressing" the contrast range of the displayed data into a narrower band of the available contrast range, and "flattening" the appearance. There are no limits to the maximum value of the window width, or to the minimum or maximum value of window level, both of which may exceed the actual or possible range of input values.
- Input values "below" the window are displayed as the minimum output value and input values "above" the window are displayed as the maximum output value. This is the common usage of the window operation in medical imaging. There is no provision for an alternative approach in which all values "outside" the window are displayed as the minimum output value.
- The output of the Window Center/Width or VOI LUT transformation is either implicitly scaled to the full range of the display device if there is no succeeding transformation defined, or implicitly scaled to the full input range of the succeeding transformation step (such as the Presentation LUT), if present. See Section C.11.6.1.
- Fractional values of Window Center and Window Width are permitted (since the VR of these Attributes is Decimal String), and though they are not often encountered, applications should be prepared to accept them.
The Window Center (0028,1050), Window Width (0028,1051) and VOI LUT Function (0028,1056) Attributes shall be used only for Images with Photometric Interpretation (0028,0004) values of MONOCHROME1 and MONOCHROME2. They have no meaning for other Images.
If multiple values are present, both Attributes shall have the same number of values and shall be considered as pairs. Multiple values indicate that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If any VOI LUT Table is included by an Image, a Window Width and Window Center or the VOI LUT Table, but not both, may be applied to the Image for display. Inclusion of both indicates that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If multiple Items are present in VOI LUT Sequence (0028,3010), only one may be applied to the Image for display. Multiple Items indicate that multiple alternative views may be presented.
If the VOI LUT Module is defined in an IOD and if neither a VOI LUT Sequence nor a Window Width and Window Center are present, then the VOI LUT stage of the grayscale pipeline is defined to be an identity transformation.
Note
- This requirement is specified so that IODs that define a particular output space for the grayscale pipeline, such as P-Values, are not in an undefined state when no VOI LUT Sequence or Window Width and Window Center are present.
- Despite the Type 3 requirement for VOI LUT Sequence and Window Center, implementations that render images are expected to implement and apply these transformations when they are present in the image, unless overridden by the user, a presentation state, or a hanging protocol, and to allow the user to select which transformation to apply when multiple transformations are present.
7. Rescale Intercept Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values
| (0028,1052) |
| Required (1) |
| RescaleIntercept |
| 1 |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
The value b in relationship between stored values (SV) and the output units.
Output units = m*SV+b
If Image Type (0008,0008) Value 1 is ORIGINAL and Value 3 is not LOCALIZER, and Multi-energy CT Acquisition (0018,9361) is either absent or NO, output units shall be Hounsfield Units (HU).
8. Rescale Slope Attribute
TagTypeKeywordValue MultiplicityValue RepresentationExample Values
| (0028,1053) |
| Required (1) |
| RescaleSlope |
| 1 |
| Decimal String (DS) |
|
m in the equation specified in Rescale Intercept (0028,1052).
'컴퓨터쟁이 > Bioinformatics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DICOM image 회전 시키기 (0) | 2022.02.15 |
|---|---|
| DICOM preprocessing (0) | 2022.02.14 |
| DICOM metadata 확인 (0) | 2022.02.14 |
| [용어정리] IC50, EC50, potency (0) | 2021.03.03 |
| WGCNA Tutorial (0) | 2021.02.03 |

